Creating Tasks
Each gulp task is an asynchronous JavaScript function - a function that accepts an error-first callback or returns a stream, promise, event emitter, child process, or observable (more on that later). Due to some platform limitations, synchronous tasks aren't supported, though there is a pretty nifty alternative.
Exporting
Tasks can be considered public or private.
- Public tasks are exported from your gulpfile, which allows them to be run by the
gulpcommand. - Private tasks are made to be used internally, usually used as part of
series()orparallel()composition.
A private task looks and acts like any other task, but an end-user can't ever execute it independently. To register a task publicly, export it from your gulpfile.
const { series } = require('gulp');
// The `clean` function is not exported so it can be considered a private task.
// It can still be used within the `series()` composition.
function clean(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
// The `build` function is exported so it is public and can be run with the `gulp` command.
// It can also be used within the `series()` composition.
function build(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
exports.build = build;
exports.default = series(clean, build);
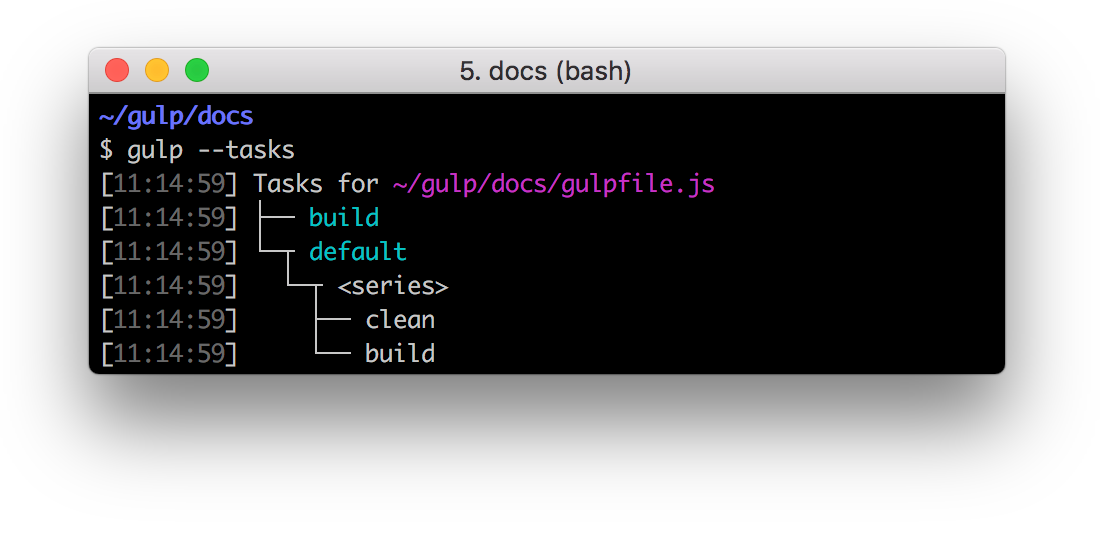
task() was used to register your functions as tasks. While that API is still available, exporting should be the primary registration mechanism, except in edge cases where exports won't work.
Compose tasks
Gulp provides two powerful composition methods, series() and parallel(), allowing individual tasks to be composed into larger operations. Both methods accept any number of task functions or composed operations. series() and parallel() can be nested within themselves or each other to any depth.
To have your tasks execute in order, use the series() method.
const { series } = require('gulp');
function transpile(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
function bundle(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
exports.build = series(transpile, bundle);
For tasks to run at maximum concurrency, combine them with the parallel() method.
const { parallel } = require('gulp');
function javascript(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
function css(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
exports.build = parallel(javascript, css);
Tasks are composed immediately when either series() or parallel() is called. This allows variation in the composition instead of conditional behavior inside individual tasks.
const { series } = require('gulp');
function minify(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
function transpile(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
function livereload(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production') {
exports.build = series(transpile, minify);
} else {
exports.build = series(transpile, livereload);
}
series() and parallel() can be nested to any arbitrary depth.
const { series, parallel } = require('gulp');
function clean(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
function cssTranspile(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
function cssMinify(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
function jsTranspile(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
function jsBundle(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
function jsMinify(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
function publish(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
exports.build = series(
clean,
parallel(
cssTranspile,
series(jsTranspile, jsBundle)
),
parallel(cssMinify, jsMinify),
publish
);
When a composed operation is run, each task will be executed every time it was referenced. For example, a clean task referenced before two different tasks would be run twice and lead to undesired results. Instead, refactor the clean task to be specified in the final composition.
If you have code like this:
// This is INCORRECT
const { series, parallel } = require('gulp');
const clean = function(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
};
const css = series(clean, function(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
});
const javascript = series(clean, function(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
});
exports.build = parallel(css, javascript);
Migrate to this:
const { series, parallel } = require('gulp');
function clean(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
function css(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
function javascript(cb) {
// body omitted
cb();
}
exports.build = series(clean, parallel(css, javascript));